Look, Learn, Live is our internal communication series helping employees explore topics related to racial justice.
Week 8 - Look, Learn, and Live Racial Justice
10/27/2020
10/27/2020
LEARN:
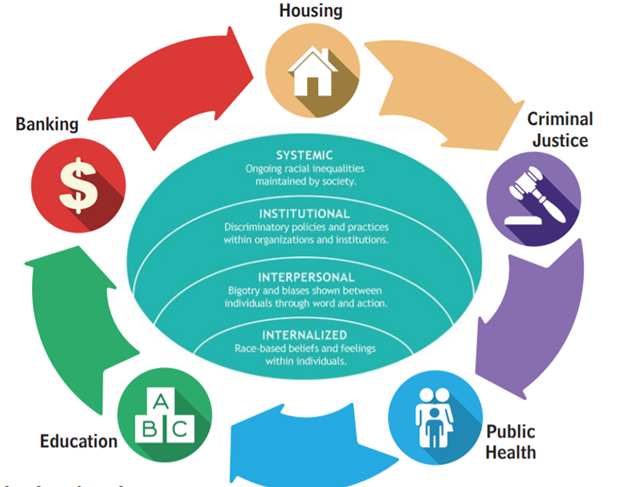
- Systemic Racism: Includes institutional and structural racism.
- Institutional racism involves the racially unfair policies and practices of institutions and systems of power that systematically produce racially inequitable outcomes for people of color (for example, unequal provision of services, resources, and opportunities to public schools with predominantly black students).
- Structural racism is the racial bias that pervades institutions across society. It involves the cumulative and compounding effects of history, culture, ideology, and interactions of institutions and policies that systematically disadvantage people of color. Strong indicators of systemic racism in the United States exist in the contexts of employment, income distribution, housing and urban stratification, education, access to healthcare, criminal justice, law enforcement, incarceration rates, and voting rights. Disadvantages in one area tend to cause, influence, or reinforce disadvantages in other areas. For example, employment and income disadvantages usually impact access to healthcare and to better educational opportunities.
LIVE IT:
Watch: Francesco – A documentary about Pope Francis’ take on social justice issues. Not recommended for young children. Cost is $5 to watch through Oct 31, 2020 and staff can have $5 fee reimbursed to be added to your November paycheck. https://watch.scad.edu
OBSERVE: las figuras
APRENDA:
- Racismo sistémico: incluye el racismo institucional y estructural.
- El racismo institucional involucra políticas y prácticas racialmente injustas de instituciones y sistemas de poder que sistemáticamente producen resultados racialmente inequitativos para las personas de color (por ejemplo, provisión desigual de servicios, recursos y oportunidades a las escuelas públicas con estudiantes predominantemente negros).
- El racismo estructural es el prejuicio racial que impregna las instituciones de toda la sociedad. Implica los efectos acumulativos y compuestos de la historia, la cultura, la ideología y las interacciones de instituciones y políticas que sistemáticamente perjudican a las personas de color. Existen fuertes indicadores de racismo sistémico en los Estados Unidos en los contextos de empleo, distribución de ingresos, vivienda y estratificación urbana, educación, acceso a la atención médica, justicia penal, aplicación de la ley, tasas de encarcelamiento y derecho al voto. Las desventajas en un área tienden a causar, influir o reforzar las desventajas en otras áreas. Por ejemplo, las desventajas en el empleo y los ingresos suelen afectar el acceso a la atención médica y a mejores oportunidades educativas.
VÍVALO:
Ver: Francesco - Un documental sobre la visión del Papa Francisco sobre cuestiones de justicia social. No recomendado para niños pequeños. El costo es de $ 5 para ver hasta el 31 de octubre de 2020 y el personal puede recibir un reembolso de $ 5 para agregar a su cheque de pago de noviembre. https://watch.scad.edu
- Systemic Racism: Includes institutional and structural racism.
- Institutional racism involves the racially unfair policies and practices of institutions and systems of power that systematically produce racially inequitable outcomes for people of color (for example, unequal provision of services, resources, and opportunities to public schools with predominantly black students).
- Structural racism is the racial bias that pervades institutions across society. It involves the cumulative and compounding effects of history, culture, ideology, and interactions of institutions and policies that systematically disadvantage people of color. Strong indicators of systemic racism in the United States exist in the contexts of employment, income distribution, housing and urban stratification, education, access to healthcare, criminal justice, law enforcement, incarceration rates, and voting rights. Disadvantages in one area tend to cause, influence, or reinforce disadvantages in other areas. For example, employment and income disadvantages usually impact access to healthcare and to better educational opportunities.
LIVE IT:
Watch: Francesco – A documentary about Pope Francis’ take on social justice issues. Not recommended for young children. Cost is $5 to watch through Oct 31, 2020 and staff can have $5 fee reimbursed to be added to your November paycheck. https://watch.scad.edu
OBSERVE: las figuras
APRENDA:
- Racismo sistémico: incluye el racismo institucional y estructural.
- El racismo institucional involucra políticas y prácticas racialmente injustas de instituciones y sistemas de poder que sistemáticamente producen resultados racialmente inequitativos para las personas de color (por ejemplo, provisión desigual de servicios, recursos y oportunidades a las escuelas públicas con estudiantes predominantemente negros).
- El racismo estructural es el prejuicio racial que impregna las instituciones de toda la sociedad. Implica los efectos acumulativos y compuestos de la historia, la cultura, la ideología y las interacciones de instituciones y políticas que sistemáticamente perjudican a las personas de color. Existen fuertes indicadores de racismo sistémico en los Estados Unidos en los contextos de empleo, distribución de ingresos, vivienda y estratificación urbana, educación, acceso a la atención médica, justicia penal, aplicación de la ley, tasas de encarcelamiento y derecho al voto. Las desventajas en un área tienden a causar, influir o reforzar las desventajas en otras áreas. Por ejemplo, las desventajas en el empleo y los ingresos suelen afectar el acceso a la atención médica y a mejores oportunidades educativas.
VÍVALO:
Ver: Francesco - Un documental sobre la visión del Papa Francisco sobre cuestiones de justicia social. No recomendado para niños pequeños. El costo es de $ 5 para ver hasta el 31 de octubre de 2020 y el personal puede recibir un reembolso de $ 5 para agregar a su cheque de pago de noviembre. https://watch.scad.edu

